- Hotline: 852+ 2891 9689
- Whatsapp: 852+ 9146 8426
- [email protected]
- 6/F 29 Austin Road, Tsimshatsui, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Diagnosis , Surgical Plan, and Corrective Solutions
Home » Hair Transplant Repair
A failure is not just poor growth. It is any result that looks unnatural, causes scarring, or wastes donor hair, including:
Unnatural Hairline: Too straight, too low, or “pluggy” looking.
Poor Graft Survival: Less than 70% of transplanted hairs grow.
Visible Scarring: Obvious linear (FUT) or patchy, over-harvested (FUE) donor areas.
Poor Density: Sparse, patchy coverage that doesn’t meet aesthetic goals.
Donor Area Depletion: Over-harvested donor zone with visible thinning.
Shock Loss Without Regrowth: Permanent loss of existing native hair around grafts.
Misdiagnosis: Transplant performed for an unsuitable condition (e.g., active scarring alopecia).
 Sara’s Comment
Sara’s CommentCan a failed hair transplant be fixed? Yes, in many cases, but successful repair depends on an accurate diagnosis of the failure and careful management of your remaining, finite donor supply. We specialize in correcting unnatural hairlines, poor density, visible scarring, and other outcomes of poor prior surgery.

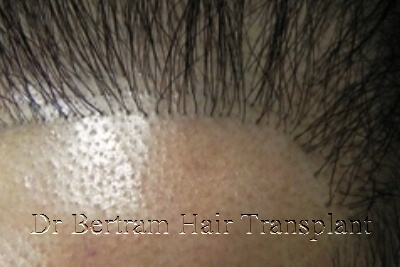
Not all failures can be fully corrected. Here’s a classification of the eight major causes of failed hair transplants into three categories — suitable, conditionally suitable, and unsuitable — for repair via hair transplant surgery :
| Category | Examples | Repair Feasibility |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ Suitable for Repair | Unnatural hairline, Poor density, Isolated visible scarring. | High success rate. Requires sufficient donor hair and expert redesign. |
| ⚠️ Conditionally Suitable | Poor graft survival, Donor depletion, Shock loss. | Possible with limitations. Requires careful donor assessment and medical stabilization. Expect modest improvement, not perfection. |
| ❌ Rarely Suitable | Severe necrosis, Active autoimmune disease (e.g., LPP, active AA), Advanced DUPA. | Often not advised. Priority is medical treatment, not more surgery. May consider camouflage (SMP) if stable. |
These conditions can typically be corrected with careful planning and skilled surgery:
Can be redesigned using finer grafts and better angulation.
Old grafts may be removed or redistributed (e.g. graft excision or laser hair removal if needed).
A second session can add more grafts to fill gaps.
Requires good remaining donor supply.
Scars from FUT or FUE can be camouflaged using grafts (especially scalp micropigmentation or FUE into scar).
Success depends on local blood supply and scar type (atrophic > hypertrophic > keloid).
These cases need careful assessment and selective patient acceptance:
A second transplant may help if the donor area is still intact and causes have been corrected (e.g., poor technique, storage, or handling in the first surgery).
If the surrounding native hair was already miniaturized and didn’t return, a transplant may replace what’s lost.
Patients must be stabilized medically first (finasteride, minoxidil, PRP, etc.).
Repair is limited.
May require scalp micropigmentation, body-to-scalp hair transplant, or a reduced aesthetic target (e.g., limited coverage).
These cases are generally poor candidates unless underlying issues are corrected or ruled out:
If tissue damage is extensive, transplant may not be possible.
Requires scar remodeling and vascular assessment before any repair.
Repair surgery is more complex than a first-time procedure. Our plan is built on assessment and conservation:
Comprehensive Diagnosis: We determine why the first transplant failed to avoid repeating mistakes.
Donor Inventory Audit: We map your remaining donor hair to create a realistic “Lifetime Graft Budget” for repair.
Artistic Redesign: For unnatural hairlines, we plan to add finer grafts in front of or between old plugs to soften and blend.
Strategic Graft Use: Every graft is precious. We prioritize the frontal core and hairline. Techniques may include:
Graft Redistribution: Adding density between existing transplanted hairs.
Scar Camouflage: Implanting grafts into FUT scars or using Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP).
Correction of Angulation: Placing new grafts at the correct natural angle to fix “growing straight out” issues.
Adjuvant Therapies: We incorporate treatments like PRP, Finasteride, or Minoxidil to protect existing hair and support graft survival.
Problem: “Corn Row” or Pluggy Look.
Solution: Implant single-hair follicular units between and in front of existing plugs to break up the pattern.
Problem: Low, Straight, Unnatural Hairline.
Solution: Redesign a higher, irregular hairline. New grafts are placed to create a soft transition; some old frontal grafts may be removed via FUE extraction or laser.
Problem: Poor Density & Visible Scarring.
Solution: A session focused on adding density to sparse areas, combined with FUE into scars to camouflage them.
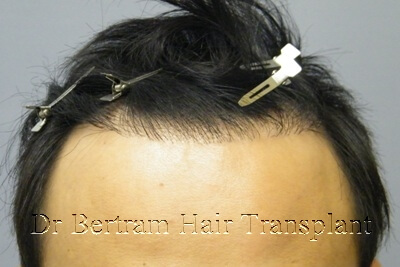
Example 1 :
Position of the hairline was reasonable, but the density was too low. Also the hairline was too rigid and orderly to be natural.
How We Fix It:
Randomly add on density in front of and amongst the existing hairs
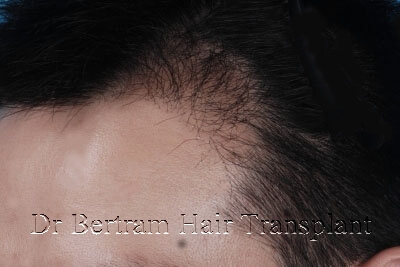
Example 2 :
The new apex was too rounded. The transplanted hairs did not match the existing ones in angles and directions.
How We Fix It:
Punch out the unwanted transplanted hairs and recycled, will leave scars
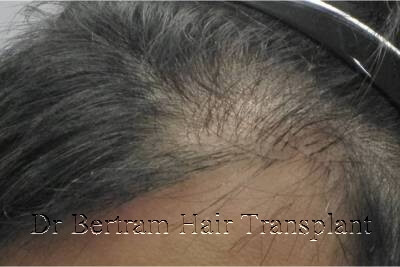
Example 3 :
Not enough grafts to fill in the center behind the hairline, creating the look of a Kappa
How We Fix It:
Simply add on the density
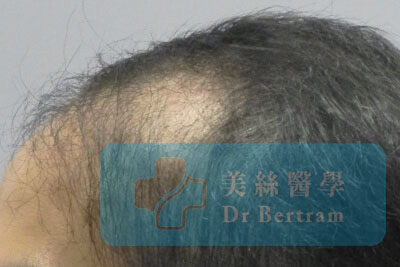
Example 4 :
There was inadequate density of grafts behind the narrow hairline.
How We Fix It:
Add more grafts in the empty area.
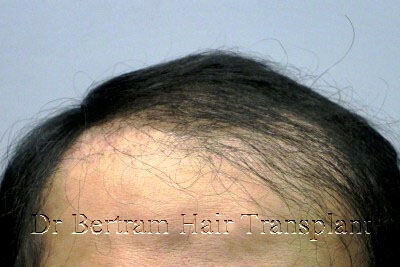
Example 5 :
Asymmetry in the hairline – the right side is higher than the left by 2cm.
How We Fix It:
Lower the right side by 1cm may improve.

Example 6 :
Difficult to style the hair as the grafts were inserted perpendicularly. Correct angle should be 35-45°.
How We Fix It:
No!

Example 7 :
The typical ‘Corn Rows” appearance, when minigrafts instead of follicular units were used. The insertion was too orderly.
How We Fix It:
Put some 1-hair FU in front, and add more grafts in between.

Example 8 :
Another typical example of the “Corn Rows” appearance. The pattern is more obvious on cutting short the hair.
How We Fix It:
Add grafts in between inorderly to be more natural looking.
The cornerstone of ethical repair is honesty.
If your donor area is severely depleted, full correction may be impossible.
Our goal is to use your remaining grafts to achieve the most significant aesthetic improvement possible, often focusing on the frontal frame.
We will never recommend a procedure that would further jeopardize your donor area for minimal gain.
Many failed hair transplants can be improved with specialized repair surgery, but outcomes depend heavily on your remaining donor hair supply.
Successful repair requires a correct diagnosis of the initial failure (e.g., poor technique vs. wrong patient selection).
The “No Regret” repair philosophy prioritizes donor conservation. We aim for significant aesthetic improvement, not necessarily perfect density.
Techniques like graft redistribution, scar camouflage, and hairline redesign are used to create a softer, more natural result.
An honest assessment is the first step. Some cases, especially those with severe donor depletion or active disease, may have very limited surgical options.
Send clear photos of your front, top, and donor areas. Our professional team will provide a preliminary assessment of what may be possible. A full in-person consultation is then essential to audit your donor supply and build a realistic corrective plan.

Images & Information shown are for reference only
Information on this website is provided for general educational purposes only and does not constitute personalized medical advice. It is not intended to promote our service or imply superiority over another.
Individual results in hair restoration vary significantly and no outcome can be guaranteed. The before-and-after images shown represent possible results — not promises. We recommend seeking independent medical advice to discuss your options … Read More
Pre-Consultation Review
If you want to get a personalized answer from our medical team, you can reach us using this form here. We will cantact you as soon as possible.
Our practice adheres to guidelines established by leading international organizations in Hair Restoration.

International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery is the leading global medical association that establishes international practice standards and patient safety protocols.

The American Board of Hair restoration Surgery represents the highest standard. To maintain rigorous certification requirements the physician must demonstrate surgical expertise.

Worls FUE InstituteI serves as the premier educational body focused exclusively on Follicular Unit Extraction methodology. The institute ensures consistent application of safe FUE.